Microbial Solutions
Home > Microbial Solutions
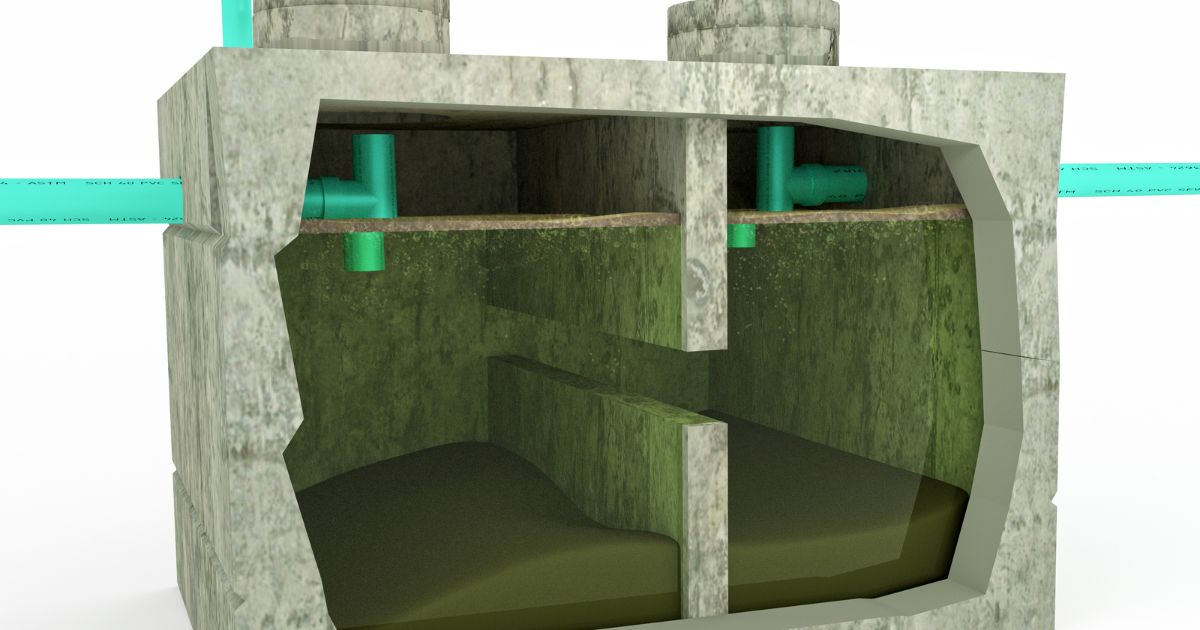

Removal of Fats, Oils and Grease in Water Treatment
Microbes play a crucial role in the removal of fats, oils, and greases (FOGs) in water treatment applications, offering an effective and sustainable solution for managing these contaminants. Certain microbial species, such as bacteria and fungi, possess the ability to break down complex organic compounds found in FOGs into simpler forms through biodegradation processes. This microbial activity is particularly valuable in wastewater treatment systems, where FOGs are common byproducts of various industries, restaurants, and households.
Microbes utilize enzymes to catalyze the breakdown of fats, oils, and greases into fatty acids and glycerol, which are more easily metabolized and assimilated by other microorganisms or removed through subsequent treatment processes.
This biodegradation not only reduces the concentration of FOGs in water but also prevents the formation of problematic substances like foam and scum.
Moreover, microbial communities in biochar-amended systems can enhance the bioremediation of FOGs by providing a favorable habitat and nutrient source for specific FOG-degrading microbes. Biochar’s porous structure and surface area create microenvironments that promote microbial colonization and activity, accelerating the degradation of FOGs and improving overall treatment efficiency.
Additionally, the use of microbes for FOG removal in water treatment aligns with sustainable practices, as it leverages natural biological processes to mitigate pollution without the need for harsh chemicals or energy-intensive methods. This microbial-based approach contributes to cleaner water resources, reduced environmental impact, and enhanced wastewater treatment performance, highlighting the importance of harnessing microbial capabilities in addressing FOG-related challenges.
Microbes, Water Treatment and Removing Organic Sediment and Sludge
Microbes play a pivotal role in water treatment processes aimed at reducing organic sediment and sludge accumulation, offering an efficient and environmentally friendly solution. Certain microbial species, including bacteria and archaea, possess the ability to metabolize organic matter present in sediments and sludge, breaking down complex compounds into simpler forms through biological processes such as biodegradation and bioconversion. This microbial activity is particularly beneficial in wastewater treatment facilities and natural water bodies where organic sediments and sludge can lead to water quality degradation, habitat disruption, and nutrient imbalances.
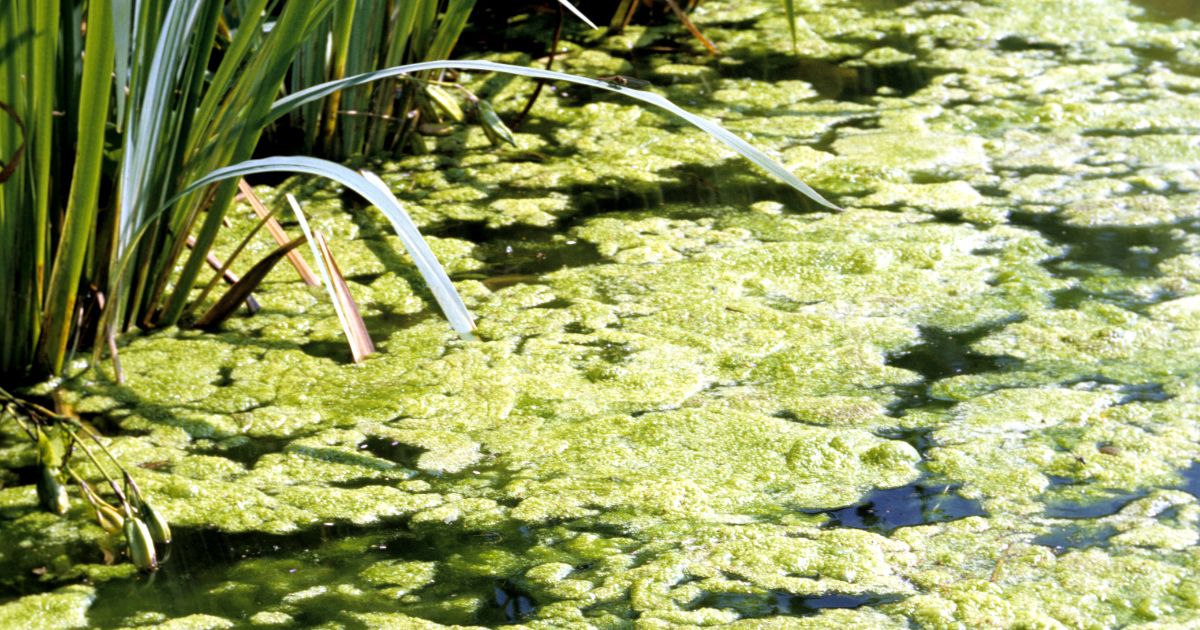

Microbes target organic materials such as dead algae, decaying plant matter, and organic pollutants, converting them into microbial biomass, gasses, and water-soluble compounds. By metabolizing these organic components, microbes reduce the overall organic load in water bodies and treatment systems, preventing the buildup of sediment layers and sludge deposits. This, in turn, improves water clarity, oxygen levels, and overall ecosystem health.
Moreover, the use of microbial consortia or bioaugmentation strategies can enhance the efficiency of organic sediment and sludge reduction in water treatment applications. Bioaugmentation involves introducing specific microbial strains or communities that are highly effective at degrading targeted organic substances, accelerating the decomposition process and minimizing sedimentation and sludge accumulation.
Furthermore, microbial-driven processes in biochar-amended systems can create favorable conditions for microbial colonization and activity, further supporting the reduction of organic sediment and sludge. Biochar’s porous structure and nutrient-retention properties enhance microbial habitat availability and nutrient cycling, promoting microbial diversity and activity.
Overall, harnessing the capabilities of microbes in water treatment for reducing organic sediment and sludge offers a sustainable and cost-effective approach that aligns with goals of environmental protection and ecosystem preservation. Integrating microbial-based strategies alongside other treatment methods enhances overall treatment efficiency and contributes to cleaner and healthier water environments.


Microbial Water Treatment Applications
Microbial use in water treatment finds diverse applications across various industries, each benefiting from tailored approaches to address specific water quality challenges. In stormwater management, microbes play a crucial role in mitigating pollutants like heavy metals, hydrocarbons, and sediment runoff. Microbial-based treatment systems can effectively break down organic pollutants and enhance sediment settling, improving the quality of stormwater runoff before it enters natural water bodies or municipal drainage systems.
In the construction industry, microbes are utilized in sediment control measures to prevent erosion, manage turbidity, and treat sediment-laden runoff from construction sites. Microbial additives and bioaugmentation techniques help stabilize soil particles, reduce sediment transport, and facilitate the breakdown of organic contaminants, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations and protecting nearby water resources.
In industrial settings, microbial applications in water treatment target a wide range of contaminants, including organic compounds, heavy metals, and industrial effluents. Bioremediation processes driven by specialized microbial consortia or bioaugmentation strategies are employed to treat wastewater, remove pollutants, and reduce sludge production, promoting sustainable practices and regulatory compliance within industries such as manufacturing, food processing, and chemical production.
Furthermore, microbial solutions are employed in natural water bodies management to restore ecological balance, control algal blooms, and improve water quality parameters. Microbial treatments for lake and pond management target excess nutrients, organic matter, and harmful algal species, supporting aquatic ecosystems and recreational water use while preserving biodiversity and water clarity.
Overall, the diverse industry applications of microbial use in water treatment highlight the versatility and effectiveness of microbial-based approaches in addressing a wide range of water quality issues, promoting environmental sustainability, and ensuring responsible water management practices across different sectors.
FAQs
Yes. Our proprietary products target organic sediments & sludges creating biological activity that will utilize that material as a food source and ultimately increase overall depth.
Yes. Microbalize can improve clarity in natural water sources by reducing the sludge material at the bottom of the water source as well as reducing excess nutrients, phosphates and ammonia.
Yes. The algae can be greatly reduced or removed all together by using bacteria to consume nutrients that the algae would otherwise use for fuel to grow.
Yes. Microbalize can benefit plant health by producing various enzymes that help make nutrients more bioavailable to the plant(s) ultimately improving overall soil health.
Yes. We Groh Land, Air & Water has a proprietary blend of microbes that will latch on to hydrocarbons and effectively turn them into water and CO2 naturally.
Ask A Question
Do you have a question or are you looking for resources related to sustainable technologies for agriculture, water treatment, and ecosystem restoration? Reach out below!

